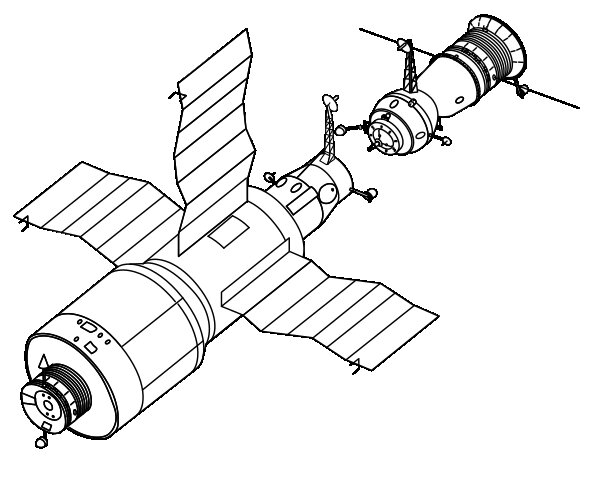
Salyut 4
Status - De-Orbited
Details
Salyut 4 represented the second phase of DOS civilian space station. Although the basic design of Salyut 1 was retained, it switched to three large solar panels mounted on the forward module rather than its predecessor's four small panels on the docking module and engine compartment, presumably to generate more power. It had an interior floor area of 34.8 sq. The pitch of the station was 2 X 59 N, yaw was 2 X 59 N and roll was 2 X 20 N. The electric System produced an average of 2.00 kW of power. It had 2,000 kg of scientific equipment alongside two sets of three solar panels each and was equipped with the Delta Navigation System which was a new autonomous navigation system that calculates orbital elements without assistance from ground. It was powered by KTDU-66 thrusters. Instrumentation
Agencies
Russian Federal Space Agency (ROSCOSMOS)
Government
Administrator: Yuri Borisov
RFSA 1992The Roscosmos State Corporation for Space Activities, commonly known as Roscosmos, is the governmental body responsible for the space science program of the Russian Federation and general aerospace research. Soyuz has many launch locations the Russian sites are Baikonur, Plesetsk and Vostochny however Ariane also purchases the vehicle and launches it from French Guiana.
Falcon 9
Crew-12
Space Launch Complex 40 - Cape Canaveral SFS, FL, USASpaceX Crew-12 is the twelfth crewed operational flight of a Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station as part of NASA's Commercial C…
Ariane 64
Amazon Leo (LE-01)
Ariane Launch Area 4 - Guiana Space Centre, French GuianaAmazon Leo, formerly known as Project Kuiper, is a mega constellation of satellites in Low Earth Orbit that will offer broadband internet access, thi…
Vulcan VC4S
USSF-87
Space Launch Complex 41 - Cape Canaveral SFS, FL, USAUSSF-87 will launch two identical Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program (GSSAP) satellites GSSAP-7 and GSSAP-8 directly to a near-geosyn…
Proton-M
Elektro-L No.5
81/24 (81P) - Baikonur Cosmodrome, Republic of KazakhstanElektro-L is a series of meteorological satellites developed for the Russian Federal Space Agency by NPO Lavochkin. They are designed to capture real…
Smart Dragon 3
PRSC-EO2 & 6 satellites
South China Sea (launch location 3) - Haiyang Oriental SpaceportCarried 7 satellites to sun-synchronous orbit, including PRSC-EO2 (Earth observation satellite for the Pakistan government's SUPARCO) & CUHK-1. Detai…

